Towards the Total Synthesis of Corallopyronine A
Markus Kalesse, Marlyse Okala Amombo, Gerald Wardenga
Corallopyronine A (1) is a natural product isolated from gliding bacteria (corallococcus coralloides) and was shown to be a potent RNA polymerase inhibitor.1 Even though the broad spectrum of activity and selectivity for bacterial RNA polymerase over the human polymerase established corallopyronie A as a promising candidate for the development as antibacterial agent, no synthetic investigations have been reported on this natural product. 2

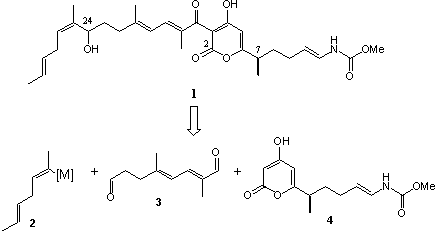
Our retrosynthetical analysis towards the total synthesis of 1 led us to three main fragments. We are planning to couple fragments 2 and 3 by asymmetric addition of organometallic reagents to aldehyde 3 using ligands such as DIANANE3 and Ephedrine. 4
The Evans-alkylation was used for the stereochemical information at C-7. The key steps in the synthesis of fragment 4 are a Lewis acid induced aldol condensation followed by DBU-induced enol lactonization to the resulting β,δ–ketoester.
Our progress towards the total synthesis of coallopyronin will be reported.
1. Reichenbach, H.; Höfle, G.; Irschik, H.; Jansen, H. Liebigs Ann. 1985, 822.
2. For synthetic efforts of myxopyronin see: Hu, T.; Schaus, J. V.; Lam, K.; Palfreyman, G. M.; Wuonola, G. G.; Panek, J. S. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 2401.
3. Paterson, I.; Sklorz, C.; Menche, D.; Berkessel, A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 1032.
4. Oppolzer, W.; Radinov, R. N. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 5777.